Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Emissions
2024 Emissions / Independent Assurance Statement

| Scope 1 (kt-CO2e) Consolidated basis (Japan) |
4.29 |
| Overseas | 0.46 |
| Total | 4.75 |
| Scope 2(kt-CO2) Consolidated basis (Japan) |
0.15 |
| Overseas | 3.74 |
| Total | 3.89 |
| Total (kt-CO2e) | 8.64 |
Energy/Carbon Dioxide(CO2)Reduction
Energy conservation measures at Headquarters building

We have installed a demand control system and a hybrid fan in the Headquarters building. When the power consumption of the Headquarters building is about to exceed the specified value, the capacity of the air conditioner is reduced to 70% by demand control, in an effort to reduce power consumption and CO2 at the same time. Moreover, a hybrid fan is mounted in all indoor units on the ceiling to circulate the temperature inside the room and make the room temperature uniform. As a result, employees working in the offices can work in an environment with less temperature irregularity, and, the room temperature can be lowered by about 10 to 20% compared to the temperature before installation. That means it provides a dual effect, including energy conservation.
Total abolition of incandescent lamps
We have stopped using the incandescent lamps for lights and we have replaced them with fluorescent tubes throughout the Headquarters building. In this manner, we are contributing to the reduction of CO2 by minimizing power consumption.
Thorough switching off of lights when not in use
We are trying to save energy by turning off the lights in workplaces when there is no work going on, such as during lunch breaks. In addition to this, we have installed sensor-type lighting on stairs and in restrooms to prevent unnecessary lighting when not in use.
Reduction of 1,700 tons of CO2 emissions by introducing cogeneration

We are trying to reduce the CO2 emissions at the private power plant installed at the Tochigi Segment by changing the fuel used from Fuel oil A to city gas. Because of this change, we were able to reduce CO2 by 1,700 tons in FY 2007 compared to FY 2005. Furthermore, the exhaust gas generated from the power plant is used to operate the air conditioner and boiler which helps to cool and heat the area inside the factory.
Green measures for the factory roof at the Tochigi Segment


A three-layered roof was created by laying heat insulating material on top of the conventional roof and then installing a new roof on top of it in order to reduce heating and cooling costs as well as to reduce greenhouse gas emissions at the slide bearings manufacturing factory at the Tochigi Segment. It’s thermal insulation effect is higher than a conventional roof, so it is effective in reducing heating and cooling costs and greenhouse gases.
Introduction of video conferencing system
We have installed video conferencing systems at our major sales offices to reduce the energy consumption required in movement of personnel. A reduction of approximately 400 kg of CO2 per meeting has been calculated.
Energy conservation at the time of installing equipment
We revised the internal rules at the time of applying for the installation of new equipment to actively introduce equipment with higher energy efficiency than the previous equipment. As a result, newly introduced equipment has achieved an energy reduction of 10% or more compared to the previous equipment.
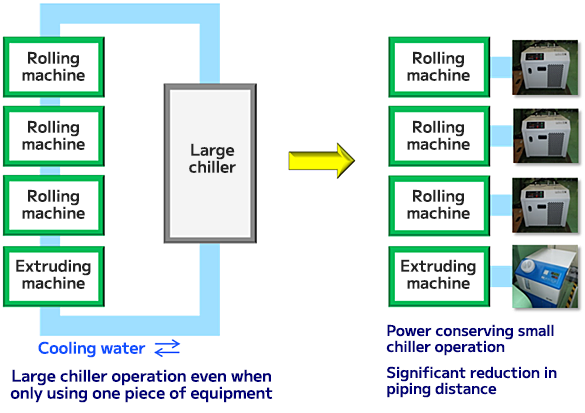
Improvement in cooling efficiency of equipment by installing a dedicated small chiller

At the Kansai Segment, the cooling water piping distance has been significantly shortened by switching from a method in which four pieces of manufacturing equipment in a rolling plant were cooled using one large chiller, to a method in which one small chiller for is provided for each piece of manufacturing equipment to cool it. The power consumption associated with cooling has been reduced significantly by operating only the relevant small chiller when using each piece of equipment. (Previous: 12.20 kW, Current: 2.13 kW). According to calculations, the amount of annual GHG reduction is equivalent to about 5% of the CO2 emissions at the Kansai Segment in FY 2016.